ネフロイドの媒介変数表示、面積、弧長の計算、アニメーションについて

1. ネフロイドとは
\[ x = a \left(3 \cos \theta – \cos3 \theta\right) \]
\[ y = a \left(3 \sin \theta – \sin3 \theta\right) \]
ここで、\(a\) は定数で、\(\theta\) は$0$から$2\pi$です。
1.1. アニメーション
ネフロイド (nephroid) は、円が固定された別の円に沿って転がることで生成される曲線です。エピサイクロイドの一種です。
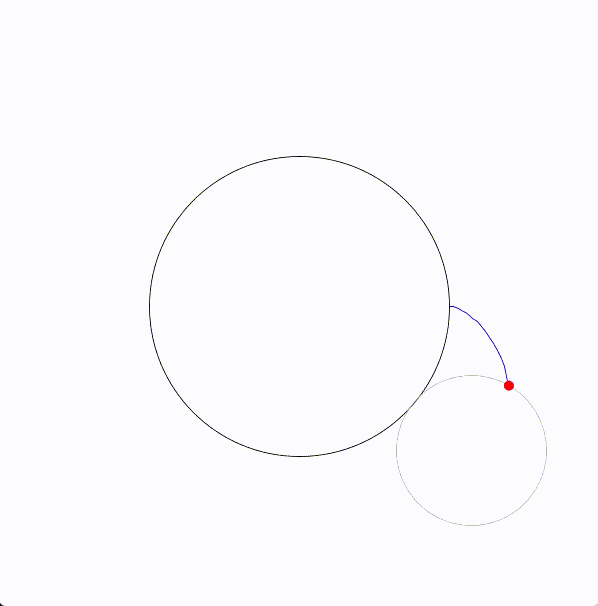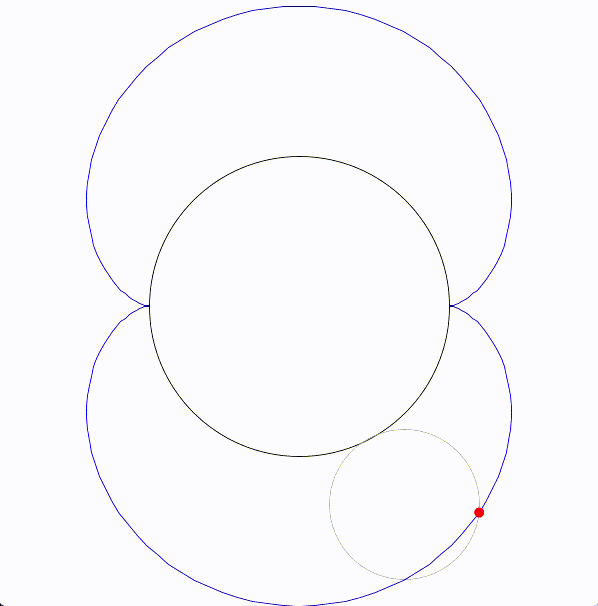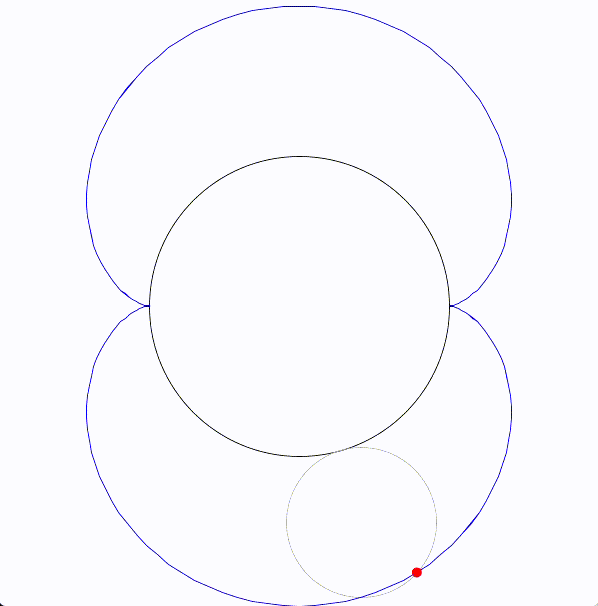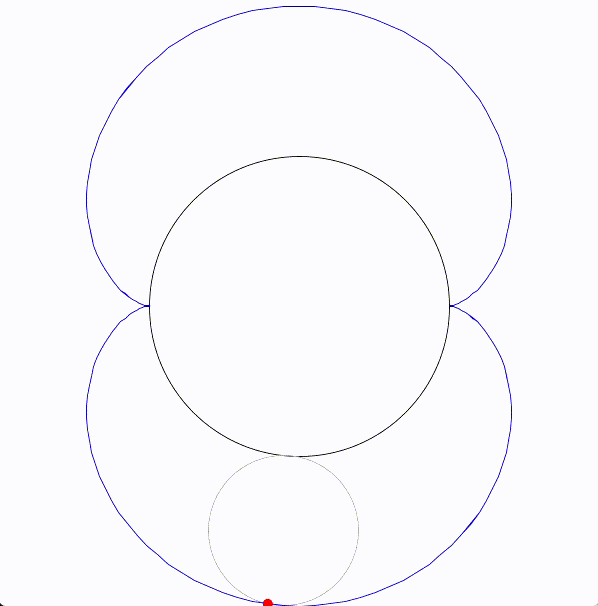
1.2. 陰曲線
\[( x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2)^3 = 108a^4y^2\]
まず、与えられた媒介変数表示
\[ x = a \left( 3 \cos \theta – \cos(3 \theta) \right) \] \[ y = a \left( 3 \sin \theta – \sin(3 \theta) \right) \]
を使って、まず \( x^2 + y^2 \) を求めましょう。
\[ x^2 = \left( a (3 \cos \theta – \cos 3 \theta) \right)^2 = a^2 \left( 9 \cos^2 \theta – 6 \cos \theta \cos 3 \theta + \cos^2 3 \theta \right) \]
\[ y^2 = \left( a (3 \sin \theta – \sin 3 \theta) \right)^2 = a^2 \left( 9 \sin^2 \theta – 6 \sin \theta \sin 3 \theta + \sin^2 3 \theta \right) \]
次に、これらを足し合わせます。
\[ x^2 + y^2 = a^2 \left( 9 \cos^2 \theta – 6 \cos \theta \cos 3 \theta + \cos^2 3 \theta \right) + a^2 \left( 9 \sin^2 \theta – 6 \sin \theta \sin 3 \theta + \sin^2 3 \theta \right) \]
これをさらに簡略化します。
まず、\( \cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta = 1 \) という恒等式を使用して、簡略化します。
\[ x^2 + y^2 = a^2 \left( 9 (\cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta) – 6 (\cos \theta \cos 3 \theta + \sin \theta \sin 3 \theta) + (\cos^2 3 \theta + \sin^2 3 \theta) \right) \]
\[ x^2 + y^2 = a^2 \left( 9 – 6 \cos(3 \theta – \theta) + 1 \right) \]
\[ x^2 + y^2 = a^2 \left( 9 – 6 \cos 2\theta + 1 \right) = a^2 \left( 10 – 6 \cos 2\theta \right) \]
次に、 \( x^2 + y^2 \) から \( 4a^2 \) を引きます。
\[ x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2 = a^2 \left( 10 – 6 \cos 2\theta \right) – 4a^2 = a^2 \left( 6 – 6 \cos 2\theta \right) \]
\[ x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2 = 6a^2 \left( 1 – \cos 2\theta \right) \]
さらに、半角の公式により、\(1 – \cos 2\theta = 2 \sin^2 \theta\) を使うと、
\[ x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2 = 12a^2 \sin^2 \theta \]
両辺を3乗すると、次のようになります。
\[( x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2)^3 = (12a^2 \sin^2 \theta)^3 \]
\[=108a^4\times 4^2a^6\sin^6\theta \]
\[=108a^4(4a\sin^3\theta)^2 \]
3倍角の公式より、$\sin 3\theta=3\sin\theta-4\sin^3\theta$となるため、
\[( x^2 + y^2 – 4a^2)^3 = 108a^4y^2\]
2. ネフロイドの性質
2.1. 面積
\[A = 12 \pi a^2\]
面積 \( A \)をガウスグリーンの定理を使って求めます。
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \int_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2} \left( x(\theta) \frac{dy(\theta)}{d\theta} – y(\theta) \frac{dx(\theta)}{d\theta} \right) d\theta \]
まず、\( x(\theta) \) と \( y(\theta) \) の微分を計算します。
\[ \frac{dx}{d\theta} = a \left( -3 \sin \theta + 3 \sin(3 \theta) \right) \]
\[ \frac{dy}{d\theta} = a \left( 3 \cos \theta – 3 \cos(3 \theta) \right) \]
公式に代入すると、次のようになります。
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \int_0^{2\pi} \left[ a \left(3 \cos \theta – \cos(3 \theta)\right) a \left(3 \cos \theta – 3 \cos(3 \theta)\right) – a \left(3 \sin \theta – \sin(3 \theta)\right) a \left(-3 \sin \theta + 3 \sin(3 \theta)\right) \right] d\theta \]
これを展開して計算します。
まず、各項を順に展開していきます。
\[ x(\theta) \frac{dy(\theta)}{d\theta} = a^2 \left( \left(3 \cos \theta – \cos(3 \theta)\right) \left(3 \cos \theta – 3 \cos(3 \theta)\right) \right) \]
\[ = a^2 \left( 9 \cos^2 \theta – 9 \cos \theta \cos(3 \theta) – 3 \cos(3 \theta) \cos \theta + 3 \cos^2(3 \theta) \right) \]
\[ y(\theta) \frac{dx(\theta)}{d\theta} = a^2 \left( \left(3 \sin \theta – \sin(3 \theta)\right) \left(-3 \sin \theta + 3 \sin(3 \theta)\right) \right) \]
\[ = a^2 \left( -9 \sin^2 \theta + 9 \sin \theta \sin(3 \theta) + 3 \sin(3 \theta) \sin \theta – 3 \sin^2(3 \theta) \right) \]
次に、これを \( 0 \) から \( 2\pi \) の範囲で積分します。
\[ A = \frac{a^2}{2} \int_0^{2\pi} \left( 9 \cos^2 \theta – 9 \cos \theta \cos(3 \theta) – 3 \cos(3 \theta) \cos \theta + 3 \cos^2(3 \theta) \right) d\theta \]
\[ – \frac{a^2}{2} \int_0^{2\pi} \left( -9 \sin^2 \theta + 9 \sin \theta \sin(3 \theta) + 3 \sin(3 \theta) \sin \theta – 3 \sin^2(3 \theta) \right) d\theta \]
ここで、三角関数の積分を計算していきます。いくつかの項が三角関数の直交性によりゼロになります。
\[ \int_0^{2\pi} \cos \theta \cos(3 \theta) d\theta = 0, \quad \int_0^{2\pi} \sin \theta \sin(3 \theta) d\theta = 0 \]
また、他の項の積分は次のようになります。
\[ \int_0^{2\pi} \cos^2 \theta d\theta = \pi, \quad \int_0^{2\pi} \cos^2(3 \theta) d\theta = \pi,\int_0^{2\pi} \sin^2 \theta d\theta = \pi, \quad \int_0^{2\pi} \sin^2(3 \theta) d\theta = \pi \]
これにより、積分は次のように簡略化されます。
\[ A = \frac{a^2}{2} \left( 12\pi + 12 \pi \right) = \frac{a^2}{2} \times 24 \pi = 12 \pi a^2 \]
よって、ネフロイドの面積は
\[ A = 12 \pi a^2 \]
です。
2.2. 弧長
\[ L = 24a \]
ネフロイドの弧長 \(L\) を求めるには、与えられた媒介変数表示を使って次の公式を適用します。
\[ L = \int_{\theta_1}^{\theta_2} \sqrt{\left( \frac{dx}{d\theta} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{dy}{d\theta} \right)^2} \, d\theta \]
まず \(x(\theta)\) と \(y(\theta)\) の導関数を計算します。
\(x(\theta)\) の導関数:
\[
\frac{dx}{d\theta} = a \left(-3 \sin \theta + 3 \sin(3 \theta)\right)
\]
\(y(\theta)\) の導関数:
\[
\frac{dy}{d\theta} = a \left(3 \cos \theta – 3 \cos(3 \theta)\right)
\]
次に、弧長公式に代入するために、それぞれの導関数の平方を計算します。
\[ \left( \frac{dx}{d\theta} \right)^2 = a^2 \left(9 \sin^2 \theta – 18 \sin \theta \sin(3 \theta) + 9 \sin^2(3 \theta)\right) \]
\[ \left( \frac{dy}{d\theta} \right)^2 = a^2 \left(9 \cos^2 \theta – 18 \cos \theta \cos(3 \theta) + 9 \cos^2(3 \theta)\right) \]
これの合計を計算します。
\[ \left( \frac{dx}{d\theta} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{dy}{d\theta} \right)^2 = a^2 \left[ 9 \left( \sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta \right) + 9 \left( \sin^2(3 \theta) + \cos^2(3 \theta) \right) – 18 \left( \sin \theta \sin(3 \theta) + \cos \theta \cos(3 \theta) \right) \right] \]
三角関数の基本恒等式 \( \sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1 \) を使うと、
\[ = a^2 \left(9 + 9 – 18 (\cos(3 \theta – \theta))\right) \]
\[ = a^2 \left(18 – 18 \cos(2 \theta)\right) \]
したがって、弧長は次の式になります。
\[ L = \int_0^{2\pi} \sqrt{a^2 \left(18 – 18 \cos(2 \theta)\right)} \, d\theta \]
\[ = a \int_0^{2\pi} \sqrt{18(1 – \cos2 \theta)} \, d\theta \]
半角の公式 \(1 – \cos(2 \theta) = 2 \sin^2(\theta)\) を使うと、
\[ L = a \int_0^{2\pi} \sqrt{36 \sin^2(\theta)} \, d\theta \]
\[ = 6a \int_0^{2\pi} |\sin(\theta)| \, d\theta \]
この積分を計算すると、結果は次の通りです。
\[ L = 24a \]
したがって、ネフロイドの弧長は \(L = 24a\) です。



